Component and Closed Cooling Water Systems
Overview
In nuclear power plants, component or closed, cooling water systems are typically used for removing heat (cooling) systems containing potentially radioactive fluids. These systems are, in turn, then cooled by the ultimate cooling system - river, lake, sea, or ocean water. In some plant designs, as the Boiling Water Reactor, the system may be divided into subsystems for each building - Turbine Building Component Cooling Water, Reactor Building Component Cooling Water. In other plant designs, as the Westinghouse Pressurized Water Reactor, the system may be considered as one regardless of where cooling occurs.
Component Cooling and Reactor Building Closed Cooling Water Systems
PWR Component Cooling (CC) Water Systems and the BWR Reactor Building Closed Cooling Water (RBCCW) Systems cool heat exchangers for:
These systems have separate subsystems, each with:
There is usually a shared tank, called a surge tank, for the redundant sub-systems is used as a makeup supply if there is not enough water in the system, or to handle the surge (increase in level) if there is too much water in the system.
Turbine Building Closed Cooling Water Systems
The BWR Turbine Building Closed Cooling Water (TBCCW) Systems cool heat exchangers for:
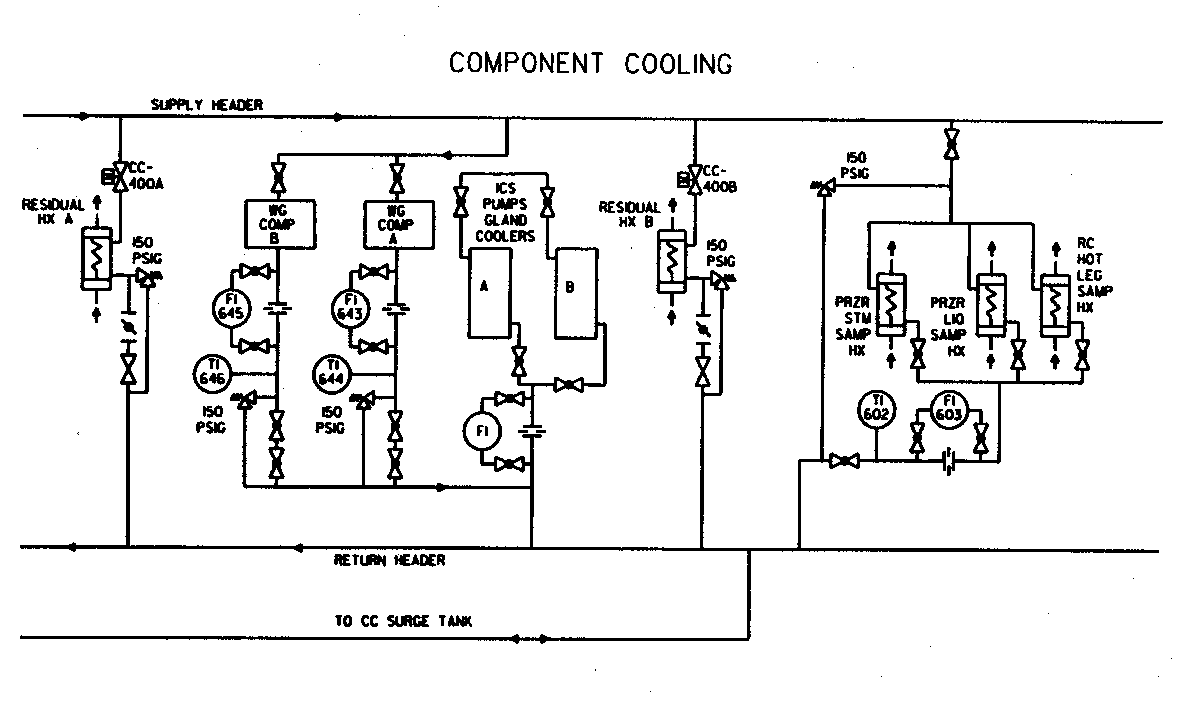
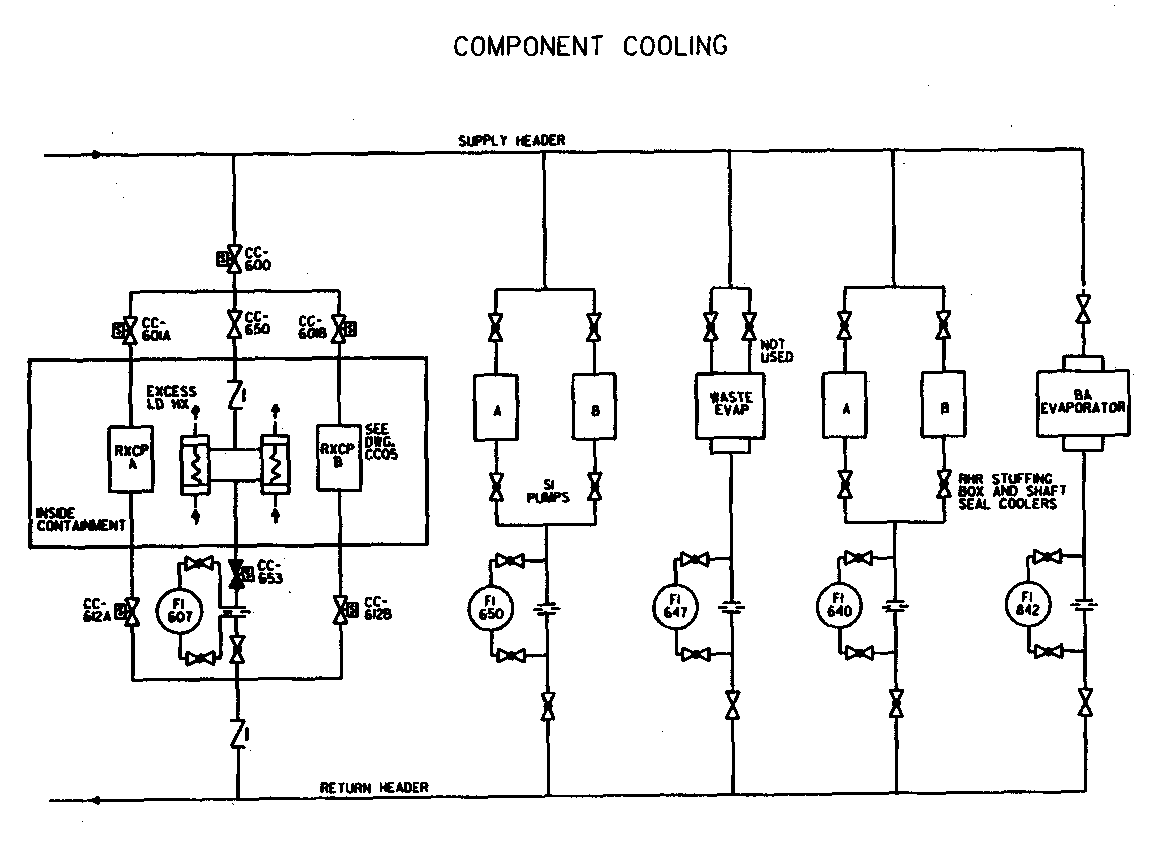
Sample System Diagram
A typical system is illustrated by the 2 diagrams below.

Copyright © 1996-2006. The Virtual Nuclear Tourist. All rights reserved. Revised: January 4, 2006.